Teachers Introduction Course to LEGO® Mindstorms NXT & EV3
(version 4.5)
UNIT 1. Course introduction: robots and technology, introduction to LEGO Technic pieces, motors, sensors and software.
The first session can be a good excuse to make students explain what they think a robot is, to talk about the difference between a robot and an automaton, to give examples of robots they know, etc.
A useful resource is to think about the different robots that appear in films and compare their features.
“Gort” in “The day the Earth stood still”, 1951


“Robby” in “Forbidden Planet”, 1956


“Data” in “Star Trek” new generation, 1966


“Hall” in “2001: a space Odyssey”, 1968
“Silent Running” ecological robots, 1972


“R2D2” or “C3PO” in “Star Wars”, 1977
Science Officer “Ash” in “Alien”, 1979
“Replicants” in “Blade Runner”, 1982


“Terminator”, 1985


“Johnny 5” in “Short Circuit”, 1986
“Matrix”, 1999


“The Bicentennial Man”, 1999


“David” in “AI”, 2001

“I Robot”, 2004


“Transformers”, 2007


“Wall-E”, 2008
Robots can be humanoid or not, good or bad, small or as big as a whole space ship, artificial, organic o cyborg, etc. At present, do we use any kind of robot? What robots do we know? Talk about examples like car wash tunnels, industrial, medical or even prosthetic robots, bomb disarming robots, autonomous vacuum cleaners, some new toys, complex traffic management equipment, elevators of a skyscraper, etc.
Explain the students the goal of the course and the knowledge they will acquire.
Open the box of each robot kit and show the different sensors, explain what they are useful for, and the different pieces, beams, connectors, gears, etc. Think about how to classify the different pieces: by colors, by size, by function? It is very important to sort out the LEGO pieces before starting to build, and it is a very good opportunity to get familiar with them.
A very interesting subject we can start introducing to the students, and that we can explain through the whole course in every pedagogical unit, is the not accidental similarity between the robots’ structure and the human body… In this sense, the intelligent brick or robot’s CPU (central processing unit) is equivalent to the human brain (the battery is equivalent the heart), the sensors would be equivalent to the sensitive system, the actuators or motors would be equivalent to the locomotion system and the cables, that connect sensors and actuators to the intelligent brick, would be equivalent to the nervous system.
Finally, you will need to build the robot that will be used to do all the exercises. The model file “model basic_0.lxf”, designed with LEGO Digital Designer (LDD) and shown in the images below, can be built with the basic education kit only.
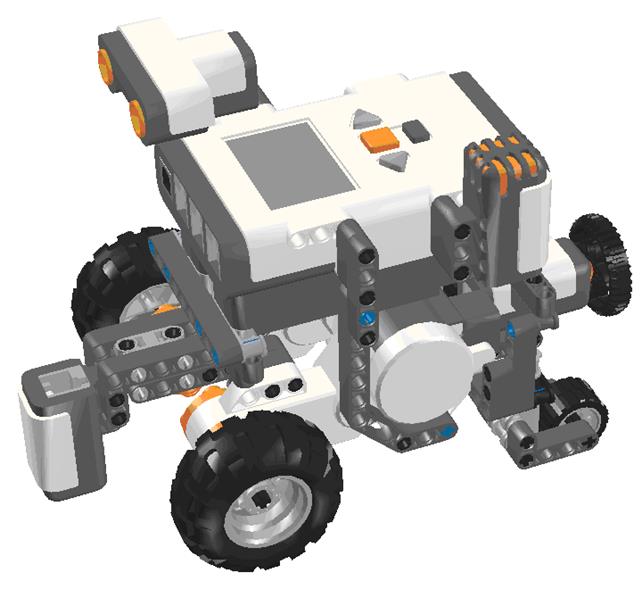

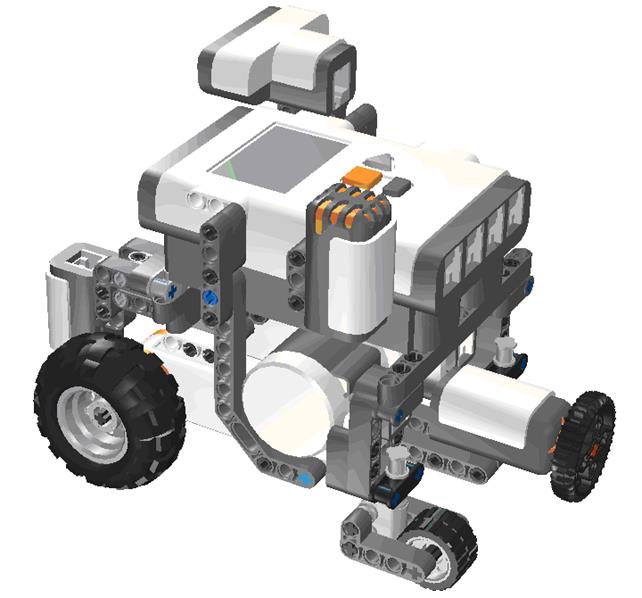
If you have the NXT resource kit, in addition of the basic kit, you can use the model improved version that you can find in the file “model basic.lxf”, shown in the following image.
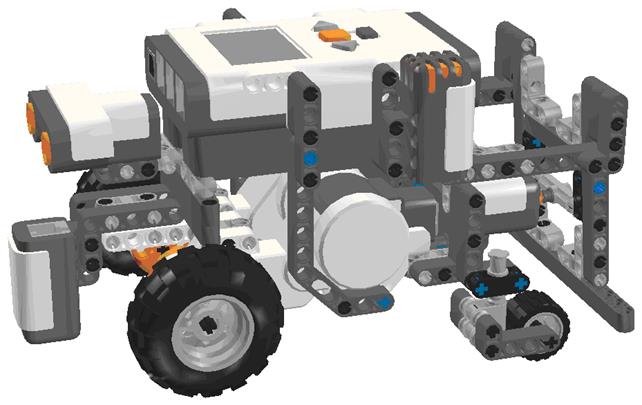
Students will get familiar with LEGO pieces and the robot parts, the motors and the sensors will be introduced later. You can use the building guide “Building Instructions [model basic_0].html” or you can open the files with LDD and build them step by step using the building guide mode.
The following Mindstorms EV3 basic robot model, very similar to the NXT one, is a modification of the education model and can be built only with the pieces of the basic education set. The file “model basic EV3_0.lxf”, built with LEGO Digital Designer (LDD), corresponds to the model of the following images.
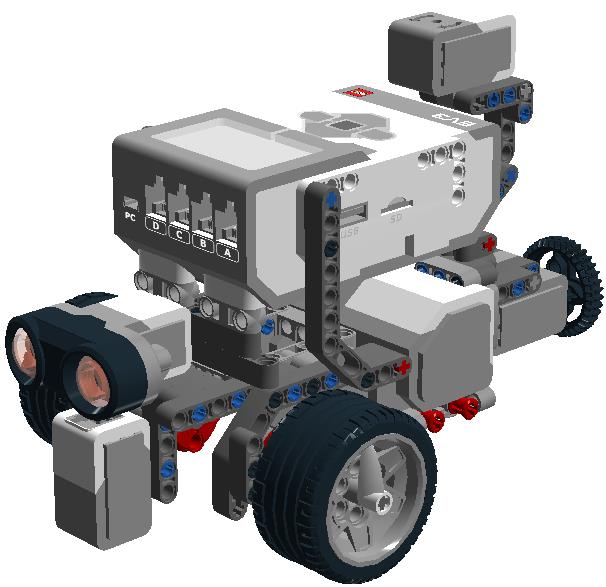

You can use the building guide “Building Instructions [model basic EV3_0].html” or you can open the files with LDD and build them step by step using the building guide mode view.
Acquired Knowledge: After completing the first pedagogical unit, the student will have an approximate idea of the course and will get fully familiar with the pieces of the LEGO robotics kit.









